Learn about Legionnaires’ disease symptoms, causes, treatment, prevention, diagnosis, risk factors, complications, and more on our website.
What is Legionnaires’ Disease?
Legionnaires’ disease can be defined as a severe form of pneumonia. Legionnaires’ disease is caused by the bacterium known as Legionella pneumophila. The disease was first discovered in 1976 during an outbreak at an American Legion convention in Philadelphia. Its name ‘Legionnaire’ was adopted from this ‘Legion’ Convention.
The disease is a serious medical condition, and understanding its basics is key. This article aims to explain its causes, symptoms, prevention, and potential complications. Having an understanding of these concepts can help in managing and reducing its impact.
From research, most types of pneumonia are commonly caused by viruses or other bacteria. However, Legionnaires’ disease is specifically linked to the Legionella bacteria. Just like pneumonia, the disease primarily affects the lungs but can also impact other parts of the body if not treated promptly.
How Legionella Bacteria Cause Disease
1. Inhalation of Aerosolized Water:
The major mode of getting Legionnaires’ disease is through inhaling aerosolized water droplets containing Legionella bacteria. Once the bacteria is present in the water, it is inhaled through mist or vapour into the lungs. This explains why sources like showers are a breeding ground for this bacteria.
2. Contaminated Water:
Once this bacterium gets into the water, it thrives, causing contamination. Therefore, direct exposure to such contaminated water can also lead to infection, particularly if the water is splashed or ingested. However, hot tubs, fountains, or other sources are less common sources.
Signs and Symptoms
Once the bacteria enters the body, it multiplies quickly. The symptoms begin to manifest within 2-10 days of exposure. What follows is a range of signs and symptoms including;
Fever
One of the major symptoms of Legionnaires’ disease is high fever. This fever occurs to signify an ongoing infection. Most of the time this fever is accompanied by chills, which can further exacerbate the discomfort. NOTE: There is another type of fever called ‘Pontiac Fever’ caused by the same genus of Legionella bacteria. However, Pontiac fever is milder compared to fever caused by Legionnaires’ disease.
Cough
A persistent cough occurs as bacteria multiply in the lungs. This cough can become heavy and often produce mucus or even blood.
Shortness of Breath
This occurs as the disease attacks the alveoli and penetrates deep tissues of the lungs. This sign can be indicative of pneumonia and may require immediate medical intervention.
Muscle Aches
General muscle pain and fatigue are commonly reported signs. They occur as immunity goes low and these symptoms are responsible for the overall sense of malaise and exhaustion.
Headache
Many individuals experience headaches that add to the discomfort of the illness.
Gastrointestinal Symptoms
The bacteria may also affect other parts of the body such as the stomach and the intestines. When this occurs, individuals experience nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. These symptoms are not always present. They can sometimes be mistaken for other gastrointestinal issues. For more symptoms caused by Legionnaires’ disease, read here: https://shorturl.at/zMHjY
Diagnosis of Legionnaires’ Disease
For effective treatment to occur, an accurate diagnosis of Legionnaires’ disease is crucial. There are several ways by which this disease can be diagnosed:
Chest X-ray
A chest X-ray is the basic and the most common way of identifying the disease. Chest X-ray helps in identifying pneumonia and assessing the extent of lung involvement. This imaging can help distinguish Legionnaires’ disease from other types of pneumonia.
Urine Test
This test detects Legionella antigens in the urine. It is a rapid and non-invasive method for diagnosing Legionnaires’ disease.
Sputum Culture
Once the bacteria enters the body, it leaves a trace in almost all body fluids. Therefore, culturing bacteria from mucus (sputum) can confirm the presence of Legionella pneumophila. This method is more specific but can take several days to yield results.
Blood Tests
This is a basic test and aims to reveal signs of infection and inflammation. It aids in providing additional clues about the severity of the disease and the body’s response.
Treatment for Legionnaires’ Disease
Legionnaires’ disease is highly treatable with antibiotics. The choice of antibiotic depends on the severity of the illness and the patient’s overall health. Timely treatment is essential to prevent complications and improve recovery outcomes. Commonly prescribed antibiotics include:
Azithromycin
Often used for mild to moderate cases, azithromycin is effective against Legionella. It is a good option to help in reducing symptoms. The drug works by effectively stopping bacterial growth and replication.
Levofloxacin
This antibiotic is commonly prescribed for more severe infections. It has a broad spectrum of activity and is effective against various bacterial pathogens. The drug works by inhibiting bacterial DNA replication and repair, thereby preventing the growth and proliferation of bacteria.
Doxycycline
Another option for treatment, doxycycline, can be used based on patient factors and antibiotic sensitivity. It works by stopping bacterial growth and reproduction. To know more about Legionnaires’ disease treatment, check this: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/17750-legionnaires-disease
Prevention of Legionnaires’ Disease
Ideally, preventing Legionnaires’ disease requires identifying the source of this bacterium first. Then, the second stage involves controlling the spread of Legionella bacteria in water systems. These key preventative strategies include:
Regular Maintenance
Legionella bacteria thrive in water pipes, hot tubs, etc. Therefore regular cleaning and maintenance of things like cooling towers, and other water systems help prevent bacterial growth. Servicing water systems regularly according to the recommended schedules can save a lot of lives.
Water Temperature Control
Legionella bacteria thrive within specific temperatures that are warm. Therefore, Keeping water temperatures above 50°C (122°F) or below 20°C (68°F) inhibits bacterial growth. Adjusting temperature and regularly monitoring water systems especially if you suspect the bacteria can inhibit its proliferation.
Proper Ventilation
Because this bacteria thrives in air conditioning units, they should be well maintained. Air conditioning units should have an effective filtration system to prevent the dispersion of contaminated water droplets. You can achieve this through proper cleaning and inspecting these systems.
Water System Treatment
Biocides are an effective way of treating the bacteria that thrive in water systems. When biocides are used well in these water treatments, they can help control and eliminate bacteria in large water systems. Use of this approach is ideal especially when dealing with overgrowth of Legionella bacteria to prevent outbreaks.
Complications of Legionnaires’ Disease
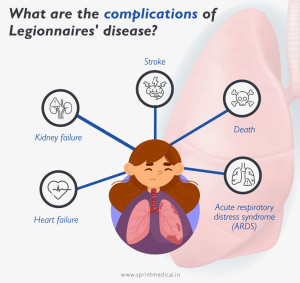
Image from: https://shorturl.at/wGYbj
When treated on time, individuals fully recover from the bacterial infection. However, if not treated promptly, Legionnaires’ disease can lead to serious complications, including:
1. Respiratory Failure
One of the major areas affected by Legionnaires’ disease is the respiratory system. With poor treatment or failure to seek medical help, the bacteria multiplies, and the infection becomes severe. Later, these severe cases may result in difficulty breathing and require mechanical ventilation. This is a critical situation that necessitates immediate medical attention.
2. Sepsis
When the bacterial overgrowth continues with no intervention, it triggers sepsis. This happens when Legionella bacteria spread from the lungs to the bloodstream, triggering a severe and widespread inflammatory response. This systemic infection overwhelms the body’s immune system, leading to organ dysfunction and potentially life-threatening septic shock. Prompt medical intervention is crucial to manage sepsis and improve outcomes for patients with severe Legionnaires disease. Sepsis is characterised by major organ dysfunction, hypotension, inadequate blood flow to the organs, etc.
3. Kidney Failure
In severe cases, the kidneys may be affected, leading to kidney failure through sepsis. What follows is systemic inflammation, low blood pressure, and blood clotting issues that reduce kidney perfusion. Bacteria growth that’s direct on the kidney tissue releases toxins that damage the kidneys further. Also, rhabdomyolysis (muscle breakdown), and dehydration contribute to kidney injury. These challenges can complicate treatment and recovery.
4. Long-Term Lung Damage
Legionnaires’ disease can cause severe pneumonia, which leads to extensive lung inflammation and damage to the alveoli. The body’s immune response to the infection releases inflammatory mediators that damage lung tissues, potentially resulting in chronic respiratory issues and reduced lung function. This also leads to decreased quality of life. To learn more about Legionannaire’s disease complications, visit here: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/legionnaires-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20351747
Who is at Risk of Contracting Legionnaires’ Disease?
Just like any other disease, Legionnaires’ disease affects some people more than others. Examples of groups that are at higher risk of contracting Legionnaires’ disease include:
1. Older Adults
Individuals over 50 years of age are more susceptible. This is because as the body ages, the immunity is reduced, exposing the older generation to many infections.
2. People with Chronic Diseases
People living with chronic diseases are at higher risk of Legionnaires’ disease. This is a result of their weakened immune systems, often caused by their underlying conditions such as asthma and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). These two for instance compromise lung function and the ability to clear infections. These illnesses push the patients to take medications that further suppress immunity. Additionally, diseases like diabetes impair immune responses and increase vulnerability to severe infections.
3. Smokers
Smoking damages the respiratory system, increasing vulnerability to respiratory infections, including Legionnaires’ disease. Smoking also causes a weakened immune system and triggers the development of COPD, all of which make it easier for Legionella bacteria to infect and damage the lungs.
4. Immunocompromised Individuals
People with weakened immune systems, such as those undergoing chemotherapy or with autoimmune diseases, are at higher risk. This is because their weakened immune systems are less able to fight off infections, making them more susceptible to severe and potentially life-threatening bacterial infections like Legionnaires’ disease.
Statistics For Legionnaires’ Disease
Understanding the scope and impact of Legionnaires’ disease is crucial for effective prevention and treatment. Here are some key statistics:
1. Incidence
According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), approximately 10,000 to 18,000 cases of Legionnaires’ disease are reported annually in the United States. However, many cases are likely underreported due to misdiagnosis or lack of testing.
2. Mortality Rate
The death rate may be as high as 40–80% in untreated immuno-suppressed patients or the elderly. However, this can be reduced to 5–30% through proper diagnosis and treatment options.
3. Hospitalization
About 90% of diagnosed cases require hospitalization. The severity of the disease often necessitates intensive medical care and monitoring.
4. Global Prevalence
The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that Legionnaires’ disease cases occur worldwide, with outbreaks reported in various countries. The exact prevalence can vary based on local water management practices and healthcare infrastructure.
5. Recent Outbreaks
Recent years have seen several significant outbreaks of Legionnaires’ disease. For example, in 2022, a major outbreak in New York City led to over 100 cases and several fatalities, highlighting the ongoing risk of large-scale incidents. Currently, the disease is present in Melbourne Australia as reported by the Australian Department of Health on 26 July 2024.
Conclusion
Legionnaires’ disease is a serious and potentially life-threatening illness caused by Legionella pneumophila. Understanding its causes, symptoms, prevention methods, and potential complications is essential for managing and reducing its impact. With timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment, most individuals recover fully. Preventing the spread of Legionella bacteria through proper maintenance of water systems and adhering to preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of infection.